
The authors are with John Finlay India Pvt Ltd.
Om Prakash- Advisor Coal & Minerals Beneficiation
Aadil Keshwani- Managing Director
Coal Beneficiation Technologies:
There are many commercially proven coal cleaning equipment and technologies available ranging from the most efficient to the least efficient ones. Our focus is on state-of-the-art technology for washing Indian coals which are infamous for difficult washability characteristics. Some Indian coals have the distinction of falling in the category of the “most difficult coals to wash.”
Given such washability characteristics and the backdrop of an array of available washing technologies, our choice gets confined to the technologies that can relate to employing coarse, small, and fine coals.
Brief Features of Technologies:
| Equipment | Applicable Size Range Feed | Basic Characteristics |
| Heavy Media Bath | 200 mm x 6 mm | Very Efficient. Insensitive to variation in feed rate. Very easy to adjust the density. Wide range of separating gravity. |
| Heavy Media Cyclone | 50 mm x 0.5 mm | Very Efficient. Insensitive to variation in feed rate. Very easy to adjust the density. Wide range of separating gravity. |
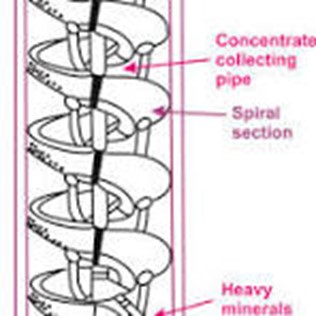
| Spirals | 3 mm x 0.5 mm | More efficient than water-only Cyclone. Separation efficiency constant. Operation at a higher solid feed percentage. |
| Flotation | Minus 0.5 mm | Produces super-clean coal. Most efficient for particle size minus 0.5 mm. |
It is found that the Heavy Media Bath and Heavy Media Cyclones of John Finlay of Australia have higher efficiencies compared to other models of heavy media baths and cyclones in the global market. Coupled with these, HM Bath & Cyclones also give higher yields of clean coal than other bath and cyclones in comparable solutions. A proven dry deshelling system for coal is also one of the technologies fortes of John Finlay.



Green Management Initiatives While Installing Coal Washery:
Viewed from the perspective of Coking Coal as well as Non-Coking Coal Washeries, in itself, are eco-friendly propositions. However, to strengthen the green measures while installing and operating the coal washery the following aspects need due consideration.
Land Environmental Problems and Remedial Initiatives:
- Land acquisition is to be thoughtfully complied with in a legally acceptable manner as per MoEF.
- Selection of site duly meeting the industrial requirement in the surrounding environment.
- Prevention of adverse impact on drainage pattern of the area and surrounding.
- Development of a factual information system in the area.
- Development of a green belt in the coal preparation plant premises by dedicating 33% of the total land area towards this and following the guidelines of CPCB.
- Strengthening of approach roads and transport parking facilities.
- Exploring the possibility of utilizing alternative building construction materials such as overburdened rocks and fly ash.
Water Environmental Problems and Remedial Initiatives:
- The coal preparation plant is to be designed and operated in a closed-circuit system to maintain zero discharge of effluents from the washing complex.
- Construction of settling pond with suitable impervious lining to prevent proclamation into groundwater. Ensure to use the settling pond only as an emergency pond and overflow if any to be recycled fully.
- Construct the garland drain all around the coal preparation plant and stockpile area.
- Provision of sewage treatment plant at the planning stage.
- Explore the possibility of covering the stockpile.
- Conservation of water by adopting a rainwater harvest system.
- Advise plant operating personnel to achieve designated water consumption norms per ton of raw coal washed.
- Use good quality flocculants to ensure minimum turbidity norms in recycled water.
Air Environmental Problems and Remedial Initiatives:
- Use of de-dusters in the washery to arrest fines before washing ROM coal.
- Provide the control system to achieve the fugitive emission standards.
- All crushers and pulverizers of the coal preparation plant are to be provided with enclosures fitted with suitable air pollution control measures.
- All strategic coal transfer points are to be provided with a water-mixed chemical spray arrangement to subside dust emissions.
- The area inside and outside of the coal preparation plant is to be made of concrete or asphalt.
- Transportation of coal by closed-body trucks/dumpers to be complied with.
- Smoke emission of the vehicles to fulfill the prescribed norms of CPCB.
- Green plantation programs all along the boundary of the coal preparation plant are to be implemented.
Solid Waste Management Problems and Remedial Initiatives:
- Extinguishing the ignited piles.
- Flattening the piles.
- Prophylactic measures prevent spontaneous ignition.
- Development of a scheme for safe handling and disposal of washery rejects.
- Utilization of rejects from coal preparation plant for mine stowing.
- Provision of suitable wind-breaking walls along the storage yard to minimize the generation of fugitive emissions.
- Development of ways and means for safe collection and disposal of solid waste from coal preparation plants.
- Planning for use of washery rejects and middling for power generation.
- Planting vegetation on waste sites is the last stage of the land re-cultivation.
Noise Environmental Problems and Remedial Initiatives:
- Installation of coal preparation equipment in such a way as to meet the noise level standards.
- Regular care of coal preparation equipment to minimize noise generation level. One such option is to follow the preventive maintenance of noise-generating machines in coal preparation plants.
- Use of silencers for air displacement equipment and DG sets.
- Selection of types of machinery to meet ambient noise standard level.
- Provision of mandatory acoustic enclosure for DG sets.
- Enclosing the process operation with rubber sheets.
Biological Environmental Problems and Remedial Initiatives:
- Conservation of rare green plants of economic importance including medicinal plants and wildlife species.
- Implementing an afforestation program to compensate for the loss of forest cover.
- Development of green belt.
- Identification of sensitive areas in the early planning stage around the site so that alternative sites can be examined.
Socioeconomic Environmental Problems and Remedial Initiatives:
- Rehabilitation and resettlement plan for project-affected families and project-displaced families.
- Budgetary provision for implementation of rehabilitation and resettlement plans.
- Imparting training for locals for employment in the project.
- Development of amenities for education and health care facilities for local people.
- Conducting socio-economic surveys to improve the quality of life.
- Set aside a considerable amount of capital outlay for sustaining green management plans.
- Educate the localities about the importance of environments and green plantations.
Conclusion:
Although it is not possible to introduce waste-free coal preparation plants all possible efforts are to be implemented to mitigate the adverse effects of environmental impacts due to land, water, air, solid waste, noise, biological, and socioeconomic. With all due respect to MoEF and CPCB for the regulatory norms in place, we ought to follow the guidelines to maintain a green environment for coal preparation plants. It is the drops that make the ocean, and every individual has an important role to play by contributing his bit not only in the control and checking the global warming but also environmental degradation. Green management initiatives can improve our quality of life to a meaningful standard.
References:
- John Finlay Products Range Brochures
- CFRI- Brochures
- Coal Processing and Utilization Textbook by D.V. Subba Rao & T. Gouricharan
- “Environmental Impact Assessment Guidance Manual for Coal Washeries prepared by ASCI, Hyderabad February 2011”.
- Published book on “Sensitivity to Climate Change Response from India” ISBN: 978•3•8383• 3228•4, Year 2010 by L. Prasad.
About Authors:
Om Prakash obtained his Master of Technology from IIT Kharagpur (India) in Mineral Engineering with a specialization in Coal Preparation in the year 1979 followed by a Postgraduate in Business Administration from Pondicherry Central University. He has been closely associated with the Denver USA technology for Coal Flotation, Separator Poland, and Fives Cail Babcock France technologies for Coal Washery projects in India.
He has the credentials of serving various reputed industry houses like Tata Steel, Triveni Engineering, Hyderabad Industries, McNally Bharat Engineering, Metso Minerals, ThyssenKrupp, and currently with John Finlay Engineering. John Finlay is a technology house for comprehensive solutions (Wet & Dry) for Coal and Mineral Beneficiation and Om Prakash has been leading a team of engineers managing Coal and Minerals processing projects and products from concept to commissioning.
Om Prakash is approachable by email: om********@********ay.in
Om Prakash is currently working as an Advisor- Coal & Minerals Beneficiation for John Finlay India Pvt Ltd.
Aadil Keshwani is working as Managing Director for John Finlay India Pvt Ltd. and has completed his Master of Computer Applications and Data-Driven Product Management from IIM Lucknow and he is also working as Product Manager for Coinstash. He is passionate about Artificial Intelligence and Machine learning and has been promoting the application of AI & ML into Coal & other mineral beneficiation.
You can reach Aadil Keshwani at aa***@********ay.in or on +91-7498986905
